明明白白我的心--mount series
时间:2010-08-17
来源:互联网
明明白白我的心--mount series(1)
文章地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2291293.html
作者:GTT
本文档归属http://oldtown.cublog.cn/.转载请注明出处!
请提出宝贵意见Mail:[email protected]
Linux Version:2.6.33
提示:本文是关于mount命令的实现!
用过Linux的人基本都用过mount命令,我最初用它,是因为想用光驱,所以得加载cdrom。当时以为
是光驱驱动程序呢,那时傻吧,linux0.11最初用的是minix FileSystem,就提供了mount命令。
文件系统是OS的很重要的一部分,如果不了解FS将对其它的子系统产生一些障碍,可大可小,例如
linux 网路协议栈这块,socket利用sockfs的实现就是文件系统的实现。
mount命令格式如下:
mount [-afFhnrvVw] [-L<标签>] [-o<选项>] [-t<文件系统类型>] [设备名] [加载点]
就不多解释了,可以man mount看看。
先看看mount的简单实现Flow
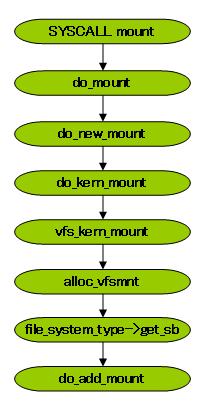
User的命令mount 是在用户空间使用的,所以利用Sys Call来实现对内核的mount的调用。
Sys Call的实现不是本文要讨论的问题,所以绕开它。就直接看内核的实现。
复制代码
dev_name就是设备文件名称,dir_name是mount的安装目录,也可以说是安装节点。type是文件系统的名称。flags是对文件系统笼统的分类,mount处理时可以分类处理了。 data是user自己设置的Option。
SYSCALL mount的代码还是比较简单的,就是从user space 得到dev_name,dir_name,data。
然后就直接调用do_mount()了
复制代码
do_mount只是根据flags进行一些简单的设定。
但是kern_path()是根据给定的目录名进行查找,这个过程很复杂,这里先忽略,以后
会详细介绍。
复制代码
例如MNT_NODEV的意思就是没有设备文件。还有只读啦等等。可以参考定义文件看看实际意义。
然后就调用do_new_mount()了。
复制代码
do_new_mount 实在是太简单了,等do_kern_mount()mount完了之后,把vfsmount
挂载到vfsmout树上。
继续...
复制代码
根据文件系统名称fstype得到对应的struct file_system_type。
然后就到vfs_kern_mount()这个过程相对比较复杂,主要分析这部分。
复制代码
这个过程太漫长,需要有一定的耐心才能看下去,代码的可读性稍微有那么点.......
自己体会吧!series(2)继续......
文章地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2291293.html
作者:GTT
本文档归属http://oldtown.cublog.cn/.转载请注明出处!
请提出宝贵意见Mail:[email protected]
Linux Version:2.6.33
提示:本文是关于mount命令的实现!
用过Linux的人基本都用过mount命令,我最初用它,是因为想用光驱,所以得加载cdrom。当时以为
是光驱驱动程序呢,那时傻吧,linux0.11最初用的是minix FileSystem,就提供了mount命令。
文件系统是OS的很重要的一部分,如果不了解FS将对其它的子系统产生一些障碍,可大可小,例如
linux 网路协议栈这块,socket利用sockfs的实现就是文件系统的实现。
mount命令格式如下:
mount [-afFhnrvVw] [-L<标签>] [-o<选项>] [-t<文件系统类型>] [设备名] [加载点]
就不多解释了,可以man mount看看。
先看看mount的简单实现Flow

User的命令mount 是在用户空间使用的,所以利用Sys Call来实现对内核的mount的调用。
Sys Call的实现不是本文要讨论的问题,所以绕开它。就直接看内核的实现。
- SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
- char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
SYSCALL mount的代码还是比较简单的,就是从user space 得到dev_name,dir_name,data。
然后就直接调用do_mount()了
- SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
- char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
- {
- int ret;
- char *kernel_type;
- char *kernel_dir;
- char *kernel_dev;
- unsigned long data_page;
-
- ret = copy_mount_string(type, &kernel_type); //从user space 拷贝文件系统类型的名称
-
- if (ret < 0) goto out_type;
-
- kernel_dir = getname(dir_name); //从user space 拷贝安装目录的名称
-
- if (IS_ERR(kernel_dir)) {
- ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dir);
- goto out_dir;
- }
-
- ret = copy_mount_string(dev_name, &kernel_dev); //从user space 拷贝设备的名称
-
- if (ret < 0) goto out_dev;
-
- ret = copy_mount_options(data, &data_page); //从user space 拷贝设置的参数
-
- if (ret < 0) goto out_data;
-
- ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, kernel_dir, kernel_type, flags, (void *) data_page);
-
- free_page(data_page);
- out_data:
- kfree(kernel_dev);
- out_dev:
- putname(kernel_dir);
- out_dir:
- kfree(kernel_type);
- out_type:
- return ret;
- }
但是kern_path()是根据给定的目录名进行查找,这个过程很复杂,这里先忽略,以后
会详细介绍。
- long do_mount(char *dev_name, char *dir_name, char *type_page,
- unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
- {
- struct path path;
- int retval = 0;
- int mnt_flags = 0;
-
- /* Discard magic */
- if ((flags & MS_MGC_MSK) == MS_MGC_VAL) flags &= ~MS_MGC_MSK;
-
- /* Basic sanity checks */
-
- if (!dir_name || !*dir_name || !memchr(dir_name, 0, PAGE_SIZE))
- return -EINVAL;
-
- if (data_page) ((char *)data_page)[PAGE_SIZE - 1] = 0;
-
- /* ... and get the mountpoint */
- retval = kern_path(dir_name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path);
- if (retval) return retval;
-
- retval = security_sb_mount(dev_name, &path, type_page, flags, data_page);
- if (retval) goto dput_out;
-
- /* Default to relatime unless overriden */
- if (!(flags & MS_NOATIME)) mnt_flags |= MNT_RELATIME;
-
- /* Separate the per-mountpoint flags */
- if (flags & MS_NOSUID) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSUID;
- if (flags & MS_NODEV) mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV;
- if (flags & MS_NOEXEC) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOEXEC;
- if (flags & MS_NOATIME) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOATIME;
- if (flags & MS_NODIRATIME) mnt_flags |= MNT_NODIRATIME;
- if (flags & MS_STRICTATIME) mnt_flags &= ~(MNT_RELATIME | MNT_NOATIME);
- if (flags & MS_RDONLY) mnt_flags |= MNT_READONLY;
-
- flags &= ~(MS_NOSUID | MS_NOEXEC | MS_NODEV | MS_ACTIVE |
- MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME| MS_KERNMOUNT |
- MS_STRICTATIME);
-
- if (flags & MS_REMOUNT)
- retval = do_remount(&path, flags & ~MS_REMOUNT, mnt_flags, data_page);
- else if (flags & MS_BIND)
- retval = do_loopback(&path, dev_name, flags & MS_REC);
- else if (flags & (MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE))
- retval = do_change_type(&path, flags);
- else if (flags & MS_MOVE)
- retval = do_move_mount(&path, dev_name);
- else
- retval = do_new_mount(&path, type_page, flags, mnt_flags, dev_name, data_page);
- dput_out:
- path_put(&path);
- return retval;
- }
然后就调用do_new_mount()了。
- static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, char *type, int flags,
- int mnt_flags, char *name, void *data)
- {
- struct vfsmount *mnt;
-
- if (!type) return -EINVAL;
-
- /* we need capabilities... */
- if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN)) return -EPERM;
-
- lock_kernel();
- mnt = do_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
- unlock_kernel();
- if (IS_ERR(mnt)) return PTR_ERR(mnt);
-
- return do_add_mount(mnt, path, mnt_flags, NULL);
- }
挂载到vfsmout树上。
继续...
- struct vfsmount * do_kern_mount(const char *fstype, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
- {
- struct file_system_type *type = get_fs_type(fstype);
- struct vfsmount *mnt;
- if (!type) return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
- mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
- if (!IS_ERR(mnt) && (type->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE) && !mnt->mnt_sb->s_subtype)
- mnt = fs_set_subtype(mnt, fstype);
- put_filesystem(type);
- return mnt;
- }
然后就到vfs_kern_mount()这个过程相对比较复杂,主要分析这部分。
- struct vfsmount * vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
- {
- struct vfsmount *mnt;
- char *secdata = NULL;
- int error;
-
- if (!type) return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
-
- error = -ENOMEM;
- mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
- if (!mnt) goto out;
-
- if (data && !(type->fs_flags & FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA)) {
- secdata = alloc_secdata();
- if (!secdata) goto out_mnt;
-
- error = security_sb_copy_data(data, secdata);
- if (error) goto out_free_secdata;
- }
-
- error = type->get_sb(type, flags, name, data, mnt);
- if (error < 0) goto out_free_secdata;
- BUG_ON(!mnt->mnt_sb);
-
- error = security_sb_kern_mount(mnt->mnt_sb, flags, secdata);
- if (error) goto out_sb;
-
- /*
- * filesystems should never set s_maxbytes larger than MAX_LFS_FILESIZE
- * but s_maxbytes was an unsigned long long for many releases. Throw
- * this warning for a little while to try and catch filesystems that
- * violate this rule. This warning should be either removed or
- * converted to a BUG() in 2.6.34.
- */
- WARN((mnt->mnt_sb->s_maxbytes < 0), "%s set sb->s_maxbytes to "
- "negative value (%lld)\n", type->name, mnt->mnt_sb->s_maxbytes);
-
- mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt_root;
- mnt->mnt_parent = mnt;
- up_write(&mnt->mnt_sb->s_umount);
- free_secdata(secdata);
- return mnt;
- out_sb:
- dput(mnt->mnt_root);
- deactivate_locked_super(mnt->mnt_sb);
- out_free_secdata:
- free_secdata(secdata);
- out_mnt:
- free_vfsmnt(mnt);
- out:
- return ERR_PTR(error);
- }
自己体会吧!series(2)继续......
作者: mtloveft 发布时间: 2010-08-17
明明白白我的心--mount series(2)
文章地址 : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2291298.html
先来看看mount的详细流程:

注册文件系统时要提供两个方法,
get_sb 和 kill_sb 分别在mount 和umount时调用。
而文件系统在内核里是以树状结构存在的,也就是
一个文件系统里可以mount其他的类型的文件系统,
当然也可以mount同类型的文件系统。
每个文件系统可以看作是VSF的一个实例。
mount文件系统就分配一个vfsmount结构。
vfsmount把各个文件系统用各种链表串起来。这样
以后查找文件系统时,根据条件在链表里查找。
命令mount 需要提供几个的参数,简单的格式如下
mount -t vfstype device dir
vfstype就是文件系统名称,device就是设备了,硬盘,cdrom,usb等等
dir 就是要安装的节点。
这个文档是分析最简单的文件系统ramfs,因为它不需要设备,
这样也不需要根buffer cache, device driver等打交道,适合了解文件系统。
不过我认为如果想掌握或者精通文件系统这块,必须分析几个文件系统,
minix比较简单,然后ext2,分析实际的文件系统,掌握这两个其它的就自然
通了,如果做网络通讯的话,sockfs也应该看看,不过有前几个文件系统的
基础的话,sockfs还是比较简单的。至于sysfs, procfs,内核开发经常用,应该
看看。不说废话了,继续分析。
第一步分配vfsmount,并初始化他的各种链表。方法名alloc_vfsmnt()
第二步分配super block, super block 简称sb,这个相当于国骂啦。我是
这个反映,或者是softbank. 为了得到super block 就调用注册文件系统时
注册的get_sb() . get_sb是个漫长的过程。不过内核VSF提供了几个通用的
得到super block 的方法。有
get_sb_nodev 没有设备文件 ramfs 等
get_sb_ns 有设备文件 minix, ext2等
get_sb_single 文件系统只有一个super block 如sysfs等
get_sb_pseudo 不能被客户端mount的文件系统sockfs, pipefs, bdev等
ramfs 是利用ram 的文件系统,所以不需要实际的设备。所以就
用get_sb_nodev这个方法了。
int get_sb_nodev(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int), struct vfsmount *mnt)
需要提供fill_super call back 方法。
ramfs的文件系统定义如下,
static struct file_system_type ramfs_fs_type = {
.name = "ramfs",
.get_sb = ramfs_get_sb,
.kill_sb = ramfs_kill_sb,
};
get_sb的定义如下
int ramfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data, struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
return get_sb_nodev(fs_type, flags, data, ramfs_fill_super, mnt);
}
所以callback 方法是 ramfs_fill_super。
文章地址 : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2291298.html
先来看看mount的详细流程:

注册文件系统时要提供两个方法,
get_sb 和 kill_sb 分别在mount 和umount时调用。
而文件系统在内核里是以树状结构存在的,也就是
一个文件系统里可以mount其他的类型的文件系统,
当然也可以mount同类型的文件系统。
每个文件系统可以看作是VSF的一个实例。
mount文件系统就分配一个vfsmount结构。
vfsmount把各个文件系统用各种链表串起来。这样
以后查找文件系统时,根据条件在链表里查找。
命令mount 需要提供几个的参数,简单的格式如下
mount -t vfstype device dir
vfstype就是文件系统名称,device就是设备了,硬盘,cdrom,usb等等
dir 就是要安装的节点。
这个文档是分析最简单的文件系统ramfs,因为它不需要设备,
这样也不需要根buffer cache, device driver等打交道,适合了解文件系统。
不过我认为如果想掌握或者精通文件系统这块,必须分析几个文件系统,
minix比较简单,然后ext2,分析实际的文件系统,掌握这两个其它的就自然
通了,如果做网络通讯的话,sockfs也应该看看,不过有前几个文件系统的
基础的话,sockfs还是比较简单的。至于sysfs, procfs,内核开发经常用,应该
看看。不说废话了,继续分析。
第一步分配vfsmount,并初始化他的各种链表。方法名alloc_vfsmnt()
第二步分配super block, super block 简称sb,这个相当于国骂啦。我是
这个反映,或者是softbank. 为了得到super block 就调用注册文件系统时
注册的get_sb() . get_sb是个漫长的过程。不过内核VSF提供了几个通用的
得到super block 的方法。有
get_sb_nodev 没有设备文件 ramfs 等
get_sb_ns 有设备文件 minix, ext2等
get_sb_single 文件系统只有一个super block 如sysfs等
get_sb_pseudo 不能被客户端mount的文件系统sockfs, pipefs, bdev等
ramfs 是利用ram 的文件系统,所以不需要实际的设备。所以就
用get_sb_nodev这个方法了。
int get_sb_nodev(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int), struct vfsmount *mnt)
需要提供fill_super call back 方法。
ramfs的文件系统定义如下,
static struct file_system_type ramfs_fs_type = {
.name = "ramfs",
.get_sb = ramfs_get_sb,
.kill_sb = ramfs_kill_sb,
};
get_sb的定义如下
int ramfs_get_sb(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data, struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
return get_sb_nodev(fs_type, flags, data, ramfs_fill_super, mnt);
}
所以callback 方法是 ramfs_fill_super。
作者: mtloveft 发布时间: 2010-08-17
明明白白我的心--mount series(3)
文章地址: http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292125.html
先把mount实现的source code贴出来,稍微注释了一点。主要是跟上一篇文章对应以下。
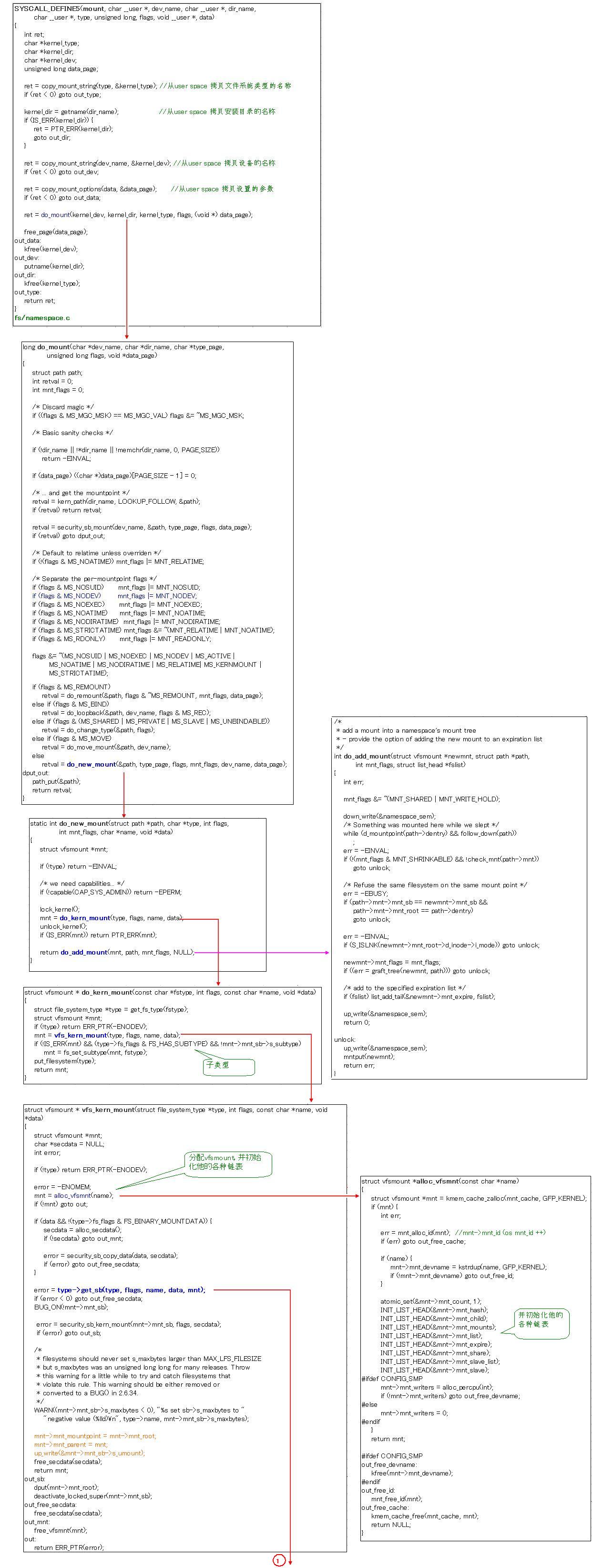
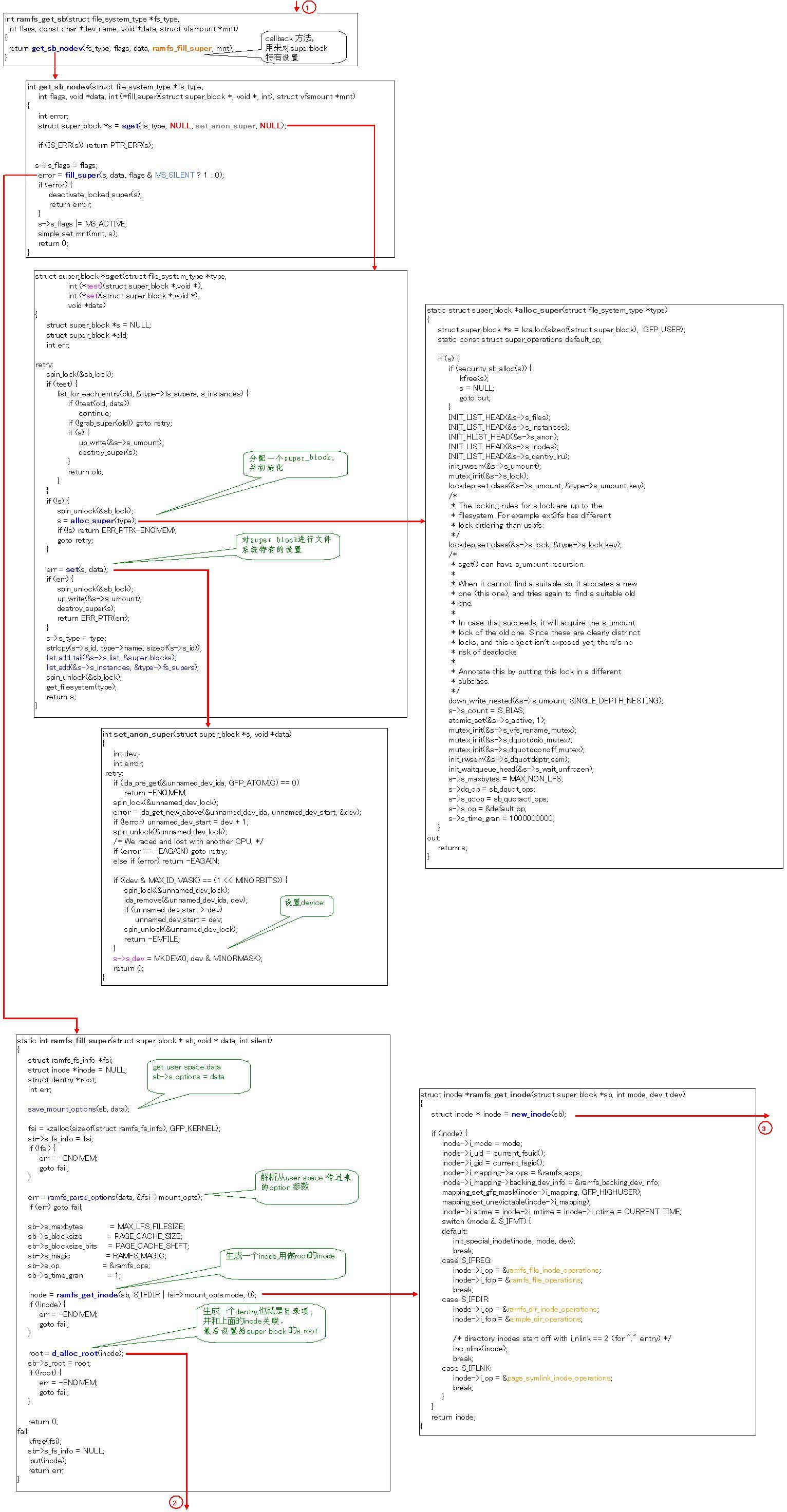
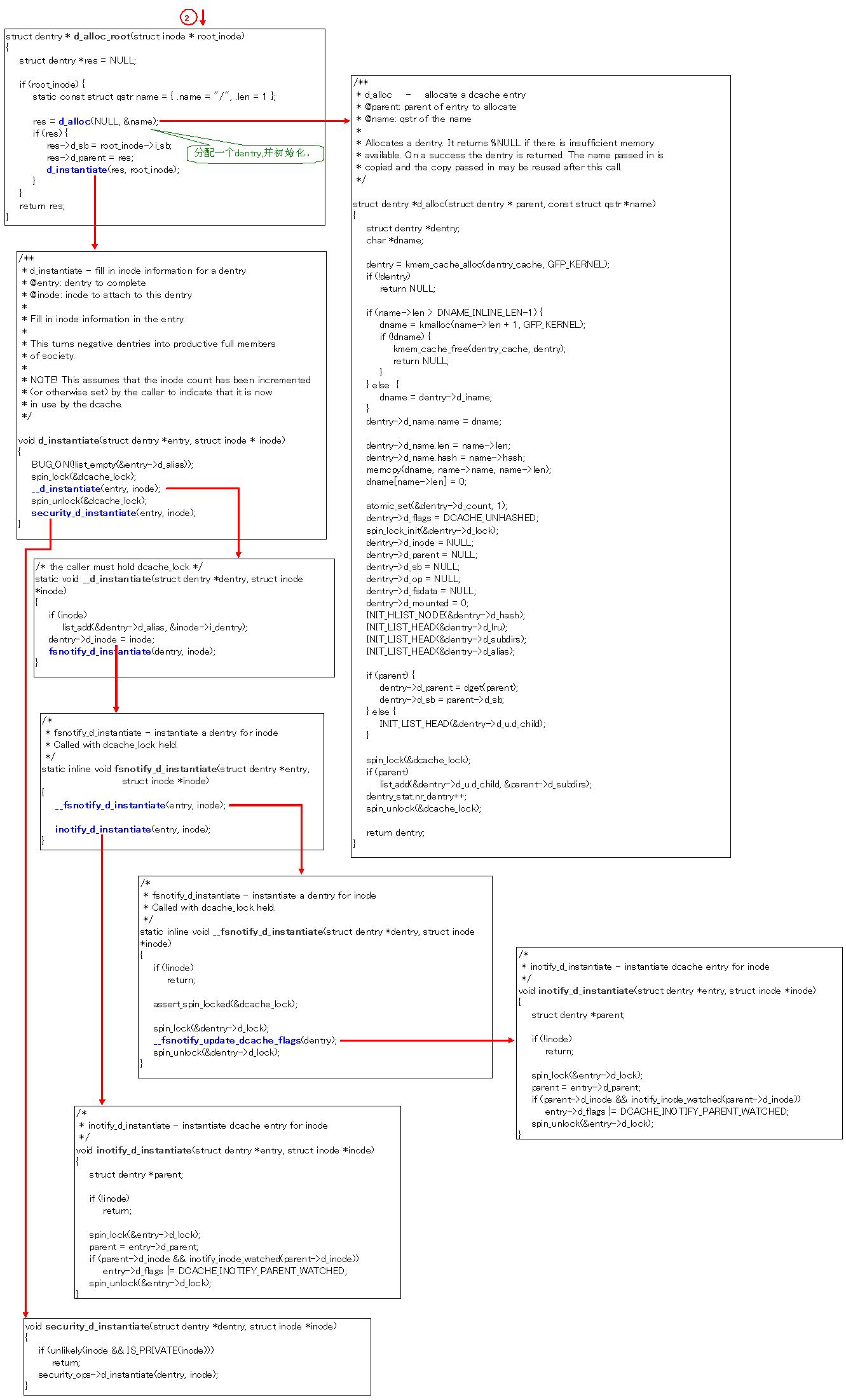

文章地址: http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292125.html
先把mount实现的source code贴出来,稍微注释了一点。主要是跟上一篇文章对应以下。




作者: mtloveft 发布时间: 2010-08-17
mount series 只是代码简单说明了一下,详细的请参看
明明白白我的心--fs series
文章地址
明明白白我的心--fs series(1) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292149.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(2) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292171.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(3) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292187.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(4) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292196.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(5) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300161.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(6) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300171.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(7) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300174.html
明明白白我的心--fs series( 8 ) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300176.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(9) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300215.html
明明白白我的心--fs series
文章地址
明明白白我的心--fs series(1) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292149.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(2) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292171.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(3) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292187.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(4) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2292196.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(5) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300161.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(6) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300171.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(7) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300174.html
明明白白我的心--fs series( 8 ) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300176.html
明明白白我的心--fs series(9) : http://blog.chinaunix.net/u3/114767/showart_2300215.html
作者: mtloveft 发布时间: 2010-08-17



楼主的图上作业做得很好啊
向楼主学习
作者: T-Bagwell 发布时间: 2010-08-17
QUOTE:
楼主的图上作业做得很好啊
向楼主学习
T-Bagwell 发表于 2010-08-17 20:30
向楼主学习
T-Bagwell 发表于 2010-08-17 20:30
一般一般啦。你的文章刚才我也看过了,很不错!
作者: mtloveft 发布时间: 2010-08-17
相关阅读 更多
热门阅读
-
 office 2019专业增强版最新2021版激活秘钥/序列号/激活码推荐 附激活工具
office 2019专业增强版最新2021版激活秘钥/序列号/激活码推荐 附激活工具
阅读:74
-
 如何安装mysql8.0
如何安装mysql8.0
阅读:31
-
 Word快速设置标题样式步骤详解
Word快速设置标题样式步骤详解
阅读:28
-
 20+道必知必会的Vue面试题(附答案解析)
20+道必知必会的Vue面试题(附答案解析)
阅读:37
-
 HTML如何制作表单
HTML如何制作表单
阅读:22
-
 百词斩可以改天数吗?当然可以,4个步骤轻松修改天数!
百词斩可以改天数吗?当然可以,4个步骤轻松修改天数!
阅读:31
-
 ET文件格式和XLS格式文件之间如何转化?
ET文件格式和XLS格式文件之间如何转化?
阅读:24
-
 react和vue的区别及优缺点是什么
react和vue的区别及优缺点是什么
阅读:121
-
 支付宝人脸识别如何关闭?
支付宝人脸识别如何关闭?
阅读:21
-
 腾讯微云怎么修改照片或视频备份路径?
腾讯微云怎么修改照片或视频备份路径?
阅读:28















